Tunnel vision is usually used to describe someone with a narrow point of view. Taken literally however, it can describe the type of vision that results with untreated glaucoma. With eye injury prevention month coming to a close next week, it seemed right to talk about ways to prevent glaucoma. This is because those with eye injury are at a higher risk of developing this condition. A recent study has found that turmeric, a natural spice, may be the golden ticket to potentially prevent glaucoma and preserve eye health.
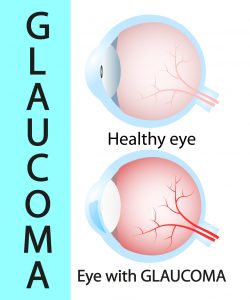 What is glaucoma?
What is glaucoma?
Glaucoma is not just one eye condition. However, it is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve and can cause vision loss and blindness. Research suggests that eye pressure is a major cause of the vision loss caused by glaucoma.
Another risk factor of optic nerve damage, and in turn, glaucoma, is high blood pressure. Even though it may seem unrelated to eat healthy to keep your eye healthy, there are blood vessels in your eye that get their blood flow from the heart. When high blood pressure constricts blood flow, it can cause pressure in the eye. In turn, this can cause vision issues.
Turmeric and glaucoma prevention
When you consider the heart health component of vision health, then turmeric as a preventive treatment makes sense. This is because turmeric is a natural anti-inflammatory agent. Since heart health issues stem from increased inflammation, then turmeric may very well benefit such conditions.
Turmeric is a root plant grown throughout Asia and Central America. It is an important part of ayurvedic medicine as a treatment for inflammatory-related conditions like pain, fatigue, arthritis, and breathing problems. Curcumin is the active ingredient in turmeric due to its antioxidant properties which help prevent cell damage that can lead to chronic disease. Although it is consumed as a spice in foods, turmeric can also be consumed in tablets, capsules, tea, or extracts.
A recent study shows that eye drops containing curcumin may help treat or prevent glaucoma. A rat study found that twice-daily use of the curcumin drops for three weeks helped reduce retinal ganglion cell loss. In other words, the eye drops helped preserve the cells in charge of delivering visual information from the eye to the brain. This study suggests that curcumin eye drops may be a treatment or preventive treatment for those at risk for glaucoma upon further study.
How to help eye health
Besides curcumin, there are things you can do today to help improve eye health.
- Eat right by consuming lots of antioxidant rich fruits and vegetables every day. This will help reduce inflammation in the body and in turn keep your eyes healthy.
- Keep your weight in a healthy range since obesity can increase risk of diabetes, which can in turn increase risk of vision loss.
- Protect your eyes with sunglasses or other eyewear like goggles or safety glasses. This is because you can prevent eye injury from sports or work accidents if your eyes are protected. Also, shielding your eyes from the UV rays of the sun can reduce eye damage.
- Quit smoking or don’t start since it can constrict blood vessels. This can in turn negatively affect blood vessel health of the eye and increase risk of eye diseases.
- Reduce screen time each day since looking at a computer, television, or phone screen too much without taking a break can put strain on the eyes. Therefore, experts suggest taking a break from the screen every 20 minutes by looking 20 feet in front of you for 20 seconds.
- Take a eye health supplement daily like Ocutain by Vita Sciences. Ocutain contains antioxidants such as lutein and beta carotene that can benefit vision health.
-written by Staci Gulbin, MS, MEd, RD, LDN
References:
Boyd, K. (April 13, 2018) “Who is at risk for glaucoma?” American Academy of Ophthalmology Online.
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (accessed July 24, 2018) “Turmeric.”
National Eye Institute (September 2015) “Facts About Glaucoma.”
National Eye Institute (accessed July 24, 2018) “Eye Health Tips.”
Science Daily (July 24, 2018) “Turmeric-derived eye drops could treat glaucoma: study.”
 Night shifts, or working from evening to morning, can be rough on your body and mind. Your meal patterns can become confused. Sleeping patterns can become thrown off course. And in turn, weight gain and sleeping issues can develop over time. A recent study has found that night shifts can cause digestive problems over time by throwing off the body’s internal clock.
Night shifts, or working from evening to morning, can be rough on your body and mind. Your meal patterns can become confused. Sleeping patterns can become thrown off course. And in turn, weight gain and sleeping issues can develop over time. A recent study has found that night shifts can cause digestive problems over time by throwing off the body’s internal clock. Now you may be saying to yourself, “Another article telling me to eat vegetables.” :sigh: However, this is not just another one of “those” articles. There are more reasons to eat your veggies than you may think. Besides providing digestive-friendly fiber and antioxidants, a recent study has shown that eating a more plant-based diet can actually lower your heart and diabetes health numbers.
Now you may be saying to yourself, “Another article telling me to eat vegetables.” :sigh: However, this is not just another one of “those” articles. There are more reasons to eat your veggies than you may think. Besides providing digestive-friendly fiber and antioxidants, a recent study has shown that eating a more plant-based diet can actually lower your heart and diabetes health numbers. Probiotics have become the talk of the town, and for good reason. Every day more research shows that taking probiotics can reduce inflammation in the gut, and in turn, may help reduce risk of inflammatory conditions such as heart disease, eczema, and inflammatory bowel disease. Therefore, adding a probiotic to your daily routine may be the answer to help free your gut, and in turn your body, from inflammation.
Probiotics have become the talk of the town, and for good reason. Every day more research shows that taking probiotics can reduce inflammation in the gut, and in turn, may help reduce risk of inflammatory conditions such as heart disease, eczema, and inflammatory bowel disease. Therefore, adding a probiotic to your daily routine may be the answer to help free your gut, and in turn your body, from inflammation.